Full extrapolation assessment
extrapolation_analysis.RdPerforms a complete evaluation of both univariate (Type I) and combinatorial (Type II) extrapolation in density surface models of line transect data, by calling relevant functions from dsmextra. As such, arguments extrapolation_analysis mirror those of the individual functions from which they are taken:
compare.arguments | Arguments from compare_covariates |
nearby.arguments | Arguments from compute_nearby |
map.arguments | Arguments from map_extrapolation |
extrapolation_analysis( samples, covariate.names, prediction.grid, coordinate.system, summarise.extrapolation = TRUE, compare.covariates = FALSE, compare.extrapolation.type = "both", compare.n.covariates = NULL, compare.create.plots = FALSE, compare.display.percent = TRUE, nearby.compute = TRUE, nearby.nearby = 1, nearby.max.size = 1e+07, nearby.no.partitions = 10, map.generate = TRUE, map.sightings = NULL, map.tracks = NULL )
Arguments
| samples | Sample (reference) dataset used for model building and calibration. This corresponds to the |
|---|---|
| covariate.names | Character string. Names of the covariates of interest. |
| prediction.grid | Prediction data.frame. This contains both geographic coordinates ( |
| coordinate.system | Projected coordinate system relevant to the study location. Can be either a character string or an object of class |
| summarise.extrapolation | Logical. If TRUE, prints a summary of extrapolation to the R console. |
| compare.covariates | Logical. If TRUE, run |
| compare.extrapolation.type | Character string indicating the type of extrapolation to be assessed. One of |
| compare.n.covariates | Integer. Maximum number of covariates. The function will compare all combinations of 1 to |
| compare.create.plots | Logical, defaults to |
| compare.display.percent | Logical, defaults to |
| nearby.compute | Logical. If TRUE, run |
| nearby.nearby | Scalar indicating which reference data points are considered to be 'nearby' (i.e. withing ‘nearby’ mean geometric Gower's distances of) prediction points. Defaults to 1. |
| nearby.max.size | Minimum size threshold for partitioning computations. Calculated as |
| nearby.no.partitions | Integer. Number of desired partitions of the data (default of 10). |
| map.generate | Logical. If TRUE, run |
| map.sightings | Species observations (optional). Can be supplied as a |
| map.tracks | Survey tracks (optional). Can be supplied as a |
References
Bouchet PJ, Miller DL, Roberts JJ, Mannocci L, Harris CM and Thomas L (2019). From here and now to there and then: Practical recommendations for extrapolating cetacean density surface models to novel conditions. CREEM Technical Report 2019-01, 59 p. https://research-repository.st-andrews.ac.uk/handle/10023/18509
Mesgaran MB, Cousens RD, Webber BL (2014). Here be dragons: a tool for quantifying novelty due to covariate range and correlation change when projecting species distribution models. Diversity & Distributions, 20: 1147-1159. DOI: 10.1111/ddi.12209
Examples
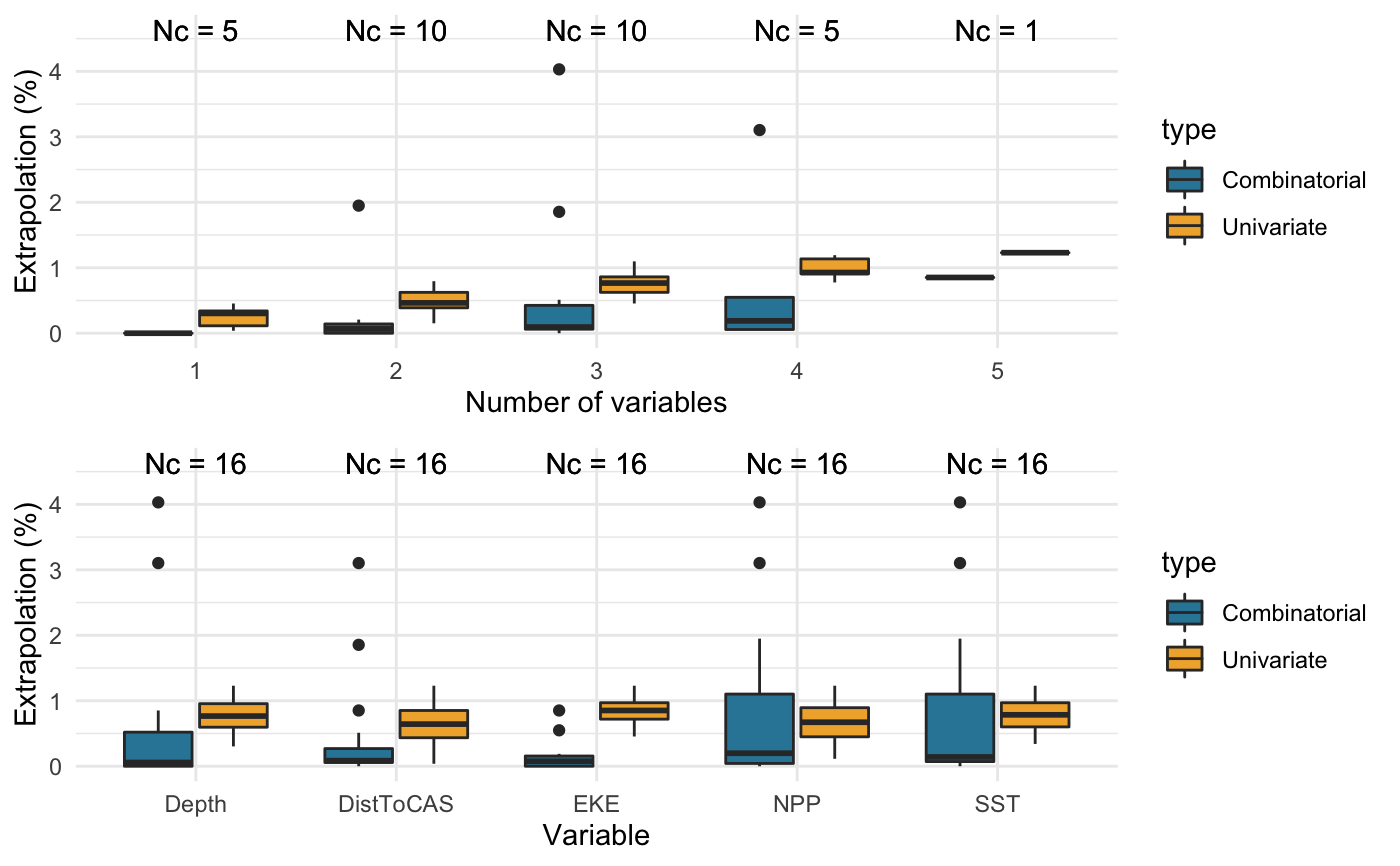
library(dsmextra) # Load the Mid-Atlantic sperm whale data (see ?spermwhales) data(spermwhales) # Extract the data segs <- spermwhales$segs predgrid <- spermwhales$predgrid # Define relevant coordinate system my_crs <- sp::CRS("+proj=aea +lat_1=38 +lat_2=30 +lat_0=34 +lon_0=-73 +x_0=0 +y_0=0 +datum=WGS84 +units=m +no_defs +ellps=WGS84 +towgs84=0,0,0") # Define covariates of interest my_cov <- c("Depth", "DistToCAS", "SST", "EKE", "NPP") spermw.analysis <- extrapolation_analysis(samples = segs, covariate.names = my_cov, prediction.grid = predgrid, coordinate.system = my_crs, summarise.extrapolation = TRUE, compare.covariates = TRUE, compare.extrapolation.type = "both", compare.n.covariates = NULL, compare.create.plots = TRUE, compare.display.percent = TRUE, nearby.compute = TRUE, nearby.nearby = 1, nearby.max.size = 1e7, nearby.no.partitions = 10, map.generate = TRUE)#>#>#>#> #>#>#>#>#>#>#> #> #> Extrapolation Minimum n_min Maximum n_max #> -------------- ----------------- ------ -------------------------------- ------ #> Univariate DistToCAS 2 Depth, DistToCAS, SST, EKE, NPP 65 #> Combinatorial Depth 0 Depth, SST, NPP 213 #> DistToCAS 0 - - #> SST 0 - - #> EKE 0 - - #> NPP 0 - - #> Depth, DistToCAS 0 - - #> Depth, EKE 0 - - #> DistToCAS, NPP 0 - - #> EKE, NPP 0 - - #> Depth, SST, EKE 0 - - #> Depth, EKE, NPP 0 - - #> Both DistToCAS 2 Depth, SST, NPP 252#> #>#>#>#>#>#>#>#> #>#> Warning: map_extrapolation relies on the leaflet package, which is built around a Web Mercator projection (EPSG:3857), and therefore requires rasters to be reprojected for plotting. As a result, minor discrepancies may occur between the interactive maps shown in the viewer, and the underlying raw data. The latter can be accessed directly from extrapolation object returned by <compute_extrapolation> and visualised using alternative packages such as ggplot2.#> Warning: map_extrapolation relies on the leaflet package, which is built around a Web Mercator projection (EPSG:3857), and therefore requires rasters to be reprojected for plotting. As a result, minor discrepancies may occur between the interactive maps shown in the viewer, and the underlying raw data. The latter can be accessed directly from extrapolation object returned by <compute_extrapolation> and visualised using alternative packages such as ggplot2.#> Warning: map_extrapolation relies on the leaflet package, which is built around a Web Mercator projection (EPSG:3857), and therefore requires rasters to be reprojected for plotting. As a result, minor discrepancies may occur between the interactive maps shown in the viewer, and the underlying raw data. The latter can be accessed directly from extrapolation object returned by <compute_extrapolation> and visualised using alternative packages such as ggplot2.#> #>